

The physiologic ventilatory dead space fraction (VD/VTphys) is usually defined as the fraction of tidal volume (VT) that does not participate in gas exchange. Dead space comprises two separate components: airway dead space (the volume of areas that do not contribute to gas exchange) and alveolar dead space (the volume of well-ventilated alveoli that receive minimal blood flow).
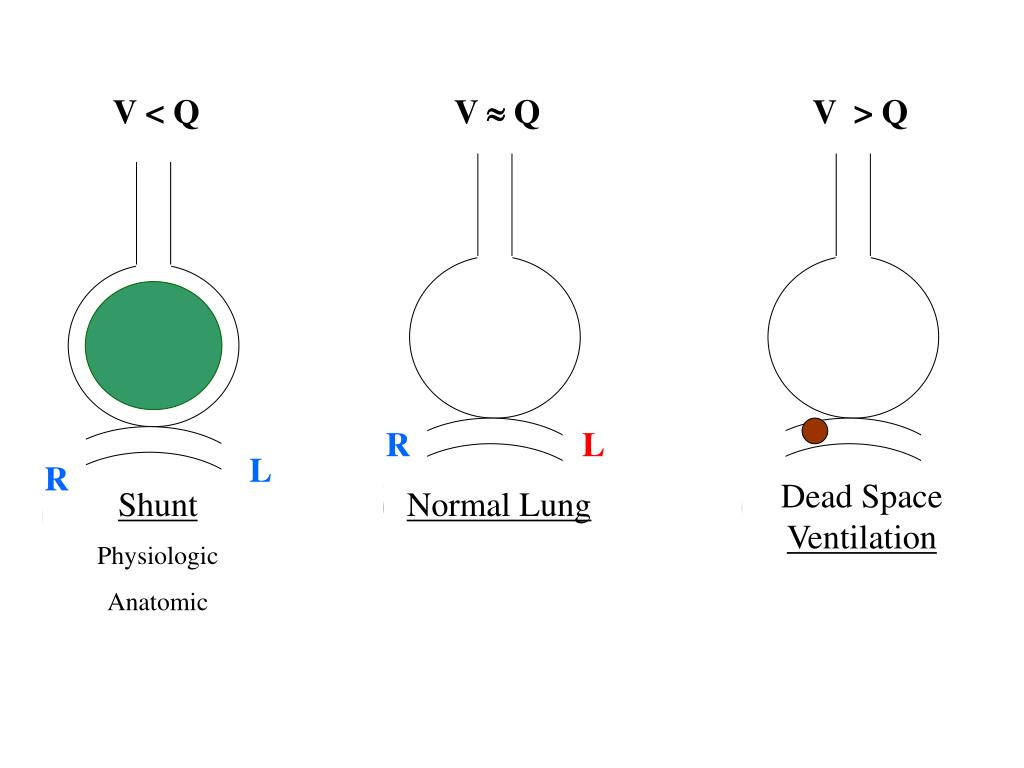
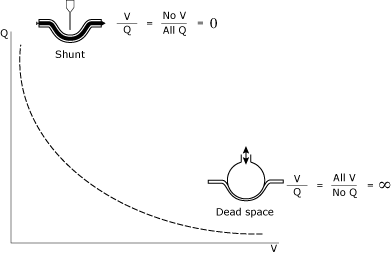
Depending on the disease condition, additional mechanisms that can contribute to an elevated physiological dead space measurement include shunt, a substantial increase in overall V'A/Q' ratio, diffusion impairment, and ventilation delivered to unperfused alveolar spaces.Dead space refers to lung areas that are ventilated but not perfused. For the range of physiological abnormalities associated with an increased physiological dead space measurement, increased alveolar ventilation/perfusion ratio (V'A/Q') heterogeneity has been the most important pathophysiological mechanism. Although a frequently cited explanation for an elevated dead space measurement has been the development of alveolar regions receiving no perfusion, evidence for this mechanism is lacking in both of these disease settings. An elevated physiological dead space, calculated from measurements of arterial CO2 and mixed expired CO2, has proven to be a useful clinical marker of prognosis both for patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome and for patients with severe heart failure.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
